Did you know that nearly half of all Americans receive health insurance coverage through either a Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) or a Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)? Understanding the differences between these two common types of health insurance plans is essential for making informed decisions about your healthcare. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of HMO and PPO health insurance, examining their coverage, cost structure, and provider networks. Join us as we explore the key factors that can help you choose the right plan for your needs.
Key Takeaways
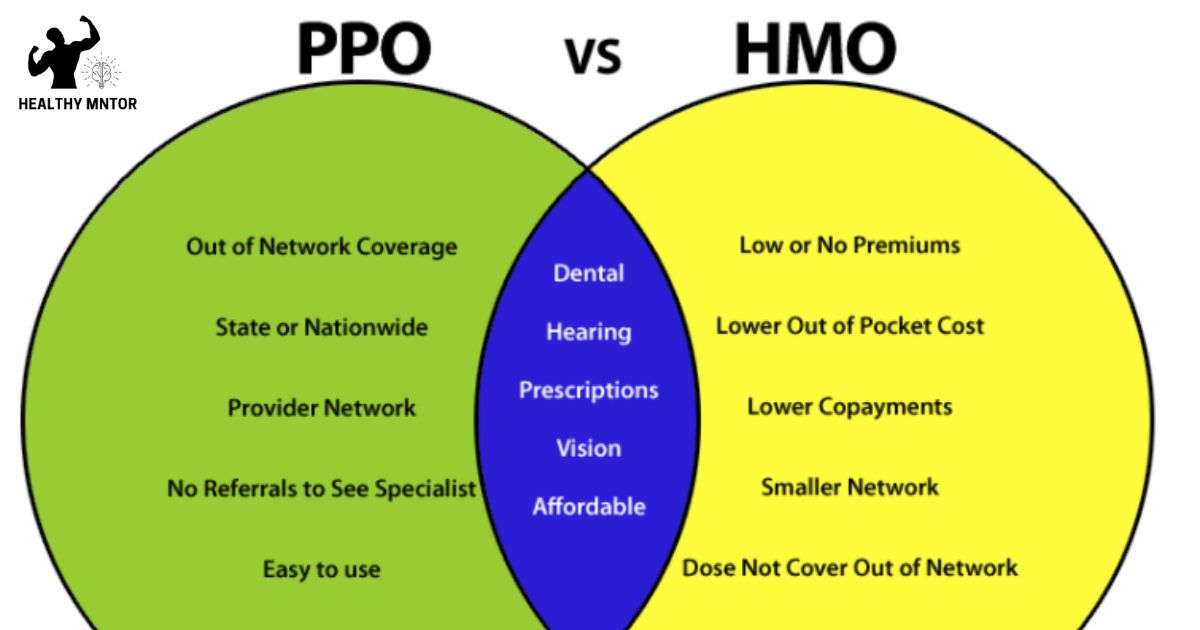
- HMO requires a primary care physician (PCP) and referrals for specialist visits, while PPO does not require a PCP or referrals.
- HMO members must receive care within a network, while PPO members can see both in-network and out-of-network providers.
- HMO has lower monthly premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs, while PPO has higher premiums but offers more flexibility in choosing providers.
- HMO focuses on cost containment, while PPO prioritizes flexibility and choice.
Definition of HMO and PPO
HMO and PPO are two different types of health insurance plans that individuals can choose from, each with its own distinct characteristics and benefits. HMO, or Health Maintenance Organization, is a managed care plan that typically requires members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain a referral from the PCP before seeing a specialist. In an HMO, members are usually required to receive care from within a network of providers, and out-of-network care is generally not covered except in emergencies. On the other hand, PPO, or Preferred Provider Organization, offers more flexibility in terms of provider choice. Members can seek care from both in-network and out-of-network providers, although the cost-sharing arrangement may differ. PPO plans generally do not require referrals for specialist visits. Understanding the differences between HMO and PPO plans is crucial in making an informed decision about which type of health insurance plan best suits one’s needs. In the following section, we will explore the coverage and network differences between HMO and PPO plans.
Coverage and Network Differences
The coverage and network differences between HMO and PPO health insurance plans can significantly impact an individual’s access to healthcare providers and the extent of coverage for medical services. Understanding these differences is crucial in making an informed decision about which plan to choose. Here are the key differences:
Coverage:
- HMO plans typically require individuals to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who acts as a gatekeeper, coordinating all medical care. Referrals from the PCP are usually necessary to see a specialist.
- PPO plans offer more flexibility, allowing individuals to see any healthcare provider without needing a referral. However, there may be higher out-of-pocket costs for out-of-network providers.
Network:
- HMO plans have a more restricted network of healthcare providers, limiting the choices available to individuals.
- PPO plans have a larger network of providers, giving individuals a wider range of options and potentially greater access to specialists.
Understanding whether a child can stay on parents’ health insurance is crucial in selecting the right health insurance plan that meets both the individual’s healthcare needs and budget.
Cost Structure and Flexibility
Cost structure and flexibility are important factors to consider when comparing HMO and PPO health insurance plans. The cost structure of an HMO plan typically involves lower monthly premiums but higher out-of-pocket costs for services. In contrast, PPO plans usually have higher monthly premiums but offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, including specialists, without requiring a referral. PPO plans also have a wider network of healthcare providers compared to HMO plans, which can be beneficial for individuals who prefer a greater choice of doctors and hospitals. Additionally, PPO plans generally provide coverage for out-of-network services, although at a higher cost. On the other hand, HMO plans focus on cost containment by emphasizing the use of in-network providers and requiring referrals for specialist care. Overall, understanding the cost structure and flexibility of HMO and PPO plans is crucial in selecting a health insurance option that aligns with individual needs and preferences.
Primary Care Physician Requirement
One important aspect to consider when comparing HMO and PPO health insurance plans is the requirement for a primary care physician. This requirement varies between the two types of plans and can have implications for the way individuals access healthcare services.
In an HMO plan:
- Individuals are typically required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) from a network of providers.
- The PCP becomes the individual’s main point of contact for all healthcare needs.
- The PCP must provide referrals for specialist care, ensuring coordination and continuity of care.
In a PPO plan:
- Individuals are not required to choose a PCP.
- They have the freedom to see any healthcare provider within or outside the network without a referral.
- However, seeing in-network providers may result in lower out-of-pocket costs.
Understanding the primary care physician requirement is essential when deciding between HMO and PPO plans, as it impacts how individuals access healthcare services and obtain specialist care. In the next section, we will explore the topic of referrals and specialist access in more detail.
Referrals and Specialist Access
Access to specialist care and obtaining referrals are key considerations when comparing HMO and PPO health insurance plans. In an HMO plan, members are typically required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who coordinates their healthcare and provides referrals to specialists when necessary. This means that to see a specialist, such as a dermatologist or cardiologist, a referral from the PCP is required. On the other hand, PPO plans generally offer more flexibility in terms of specialist access. While a referral from a PCP is not required, PPO members may still choose to consult their PCP for guidance and recommendations. This allows PPO members to directly access specialist care without the need for a referral, providing greater convenience and autonomy in managing their healthcare. Now let’s explore the next aspect of HMO and PPO plans: out-of-network coverage.
Out-of-Network Coverage
An important aspect to consider when comparing HMO and PPO health insurance plans is the extent of out-of-network coverage provided. Out-of-network coverage refers to the healthcare services received from providers who do not have a contract with the insurance plan. Here are two key points to understand about out-of-network coverage:
- HMO plans typically do not provide coverage for out-of-network services except in emergency situations. If you choose to receive care from an out-of-network provider, you may have to pay the entire cost out of pocket.
- PPO plans, on the other hand, offer more flexibility and may cover a portion of the cost for out-of-network services. However, it’s important to note that the coverage for out-of-network care is usually lower than for in-network care, and you may still be responsible for a higher percentage of the cost.
Understanding the out-of-network coverage provided by HMO and PPO plans is crucial in making an informed decision about your healthcare options.
Summary and Choosing the Right Plan
To make an informed decision about your healthcare options, it is important to consider a summary of the key differences between HMO and PPO health insurance plans and choose the right plan for your needs. HMOs, or Health Maintenance Organizations, typically offer lower premiums and require you to choose a primary care physician (PCP) who will coordinate your healthcare. With an HMO, you must obtain referrals from your PCP to see specialists, and out-of-network coverage is generally not provided except in emergencies. On the other hand, PPOs, or Preferred Provider Organizations, offer more flexibility and allow you to see any healthcare provider without a referral. PPOs also provide out-of-network coverage, although you will typically pay higher costs for this option. Ultimately, the choice between HMO and PPO health insurance plans depends on your personal healthcare needs, preferences, and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are HMO and PPO the Only Types of Health Insurance Plans Available?
There are various types of health insurance plans available in addition to HMO and PPO. These include EPO, POS, and HDHP plans, each with their own unique features and limitations.
How Do HMO and PPO Plans Differ in Terms of Prescription Drug Coverage?
HMO and PPO health insurance plans differ in terms of prescription drug coverage. HMO plans typically require primary care physician referrals and have limited drug formularies, while PPO plans offer more flexibility and broader coverage options.
Can I Switch From an HMO to a PPO Plan (Or Vice Versa) During the Year?
Yes, you can switch from an HMO to a PPO plan or vice versa during the year. However, it is important to consider factors such as network coverage, cost, and flexibility of the plans before making a switch.
Do HMO and PPO Plans Cover Mental Health and Substance Abuse Treatment?
HMO and PPO health insurance plans differ in their coverage for mental health and substance abuse treatment. Understanding the specifics of each plan is crucial to ensure comprehensive care and find the best fit for individual needs.
Are There Any Limitations on the Number of Visits or Treatments Covered by HMO and PPO Plans?
There may be limitations on the number of visits or treatments covered by HMO and PPO health insurance plans. It is important to review the specific terms and conditions of each plan to understand any restrictions or allowances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between HMO and PPO health insurance plans is crucial in making an informed decision. While both offer coverage and access to medical services, they differ in terms of network restrictions, cost structure, and flexibility. Although some may argue that HMOs provide a more cost-effective option, it is important to consider individual healthcare needs and preferences. By carefully evaluating these factors, individuals can select the plan that best suits their requirements and ensures optimal healthcare access and affordability.