In the realm of healthcare, information is a powerful weapon that must be safeguarded with utmost care. Protected Health Information (PHI) serves as the fortress that shields individuals’ personal and medical details from prying eyes, ensuring their privacy and security. With the ever-evolving landscape of technology and data, understanding the true nature of PHI becomes imperative. This article aims to shed light on the essential aspects of PHI, enlightening readers on the rights, responsibilities, and distinctions surrounding this critical realm.
Key Takeaways
- Protected Health Information (PHI) refers to individually identifiable health information created, received, maintained, or transmitted by healthcare providers.
- Compliance with privacy and security regulations, such as HIPAA, is required to safeguard PHI.
- Access controls, encryption, and regular audits are essential for maintaining the confidentiality and security of PHI.
- Non-compliance with HIPAA regulations can result in severe penalties and fines, and breaches of PHI can lead to reputational damage, legal consequences, and harm to individuals.
Definition of Protected Health Information (PHI
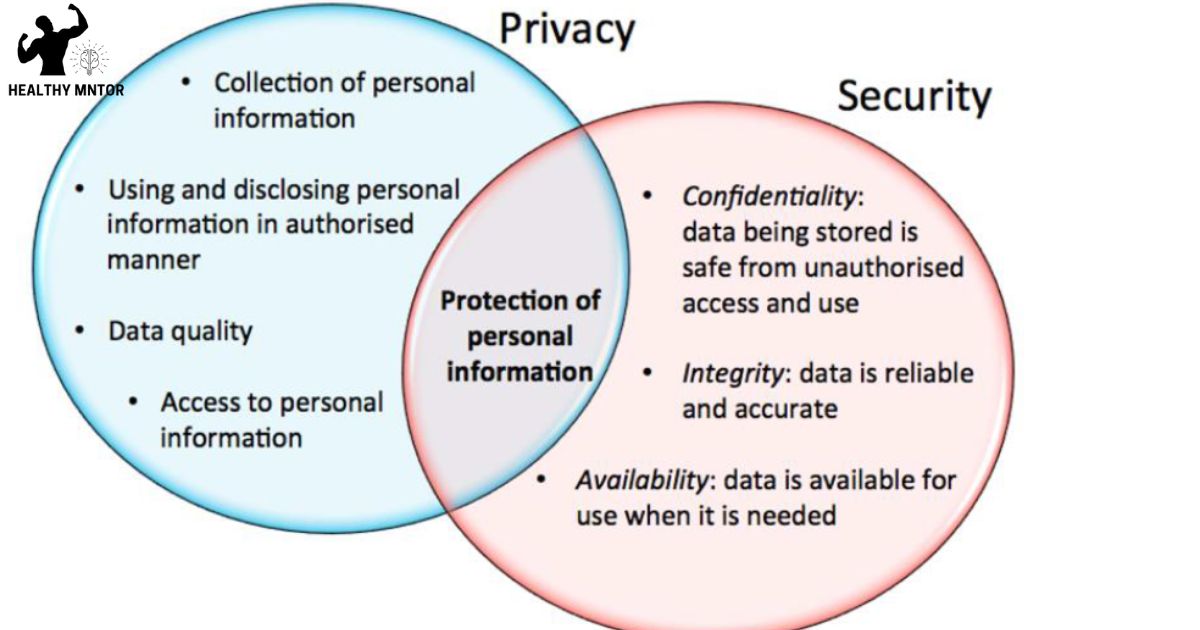
The definition of Protected Health Information (PHI) is crucial for understanding the scope of privacy and security regulations in healthcare. PHI refers to any individually identifiable health information that is created, received, maintained, or transmitted by a healthcare provider. This includes information related to a person’s physical or mental health, provision of healthcare, or payment for healthcare services. Examples of PHI include medical records, lab results, health insurance claims, and any other information that can be used to identify an individual.
The protection of PHI is of utmost importance in healthcare, as it ensures the privacy and confidentiality of patients’ personal health information. Healthcare providers and organizations must comply with strict privacy and security regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), to safeguard PHI from unauthorized access or disclosure.
Understanding the definition of PHI sets the foundation for discussing the subsequent topic of access to protected health information (PHI).
Access to Protected Health Information (PHI
Access to protected health information (PHI) is a critical concern for healthcare organizations, as it involves the handling and disclosure of individuals’ sensitive medical data. In today’s digital age, healthcare organizations must ensure that PHI is safeguarded against unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. To achieve this, organizations must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits. Additionally, healthcare professionals must adhere to strict privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which governs the collection, storage, and disclosure of PHI. Failure to protect PHI can result in severe consequences, including legal penalties, reputational damage, and loss of patient trust. Therefore, healthcare organizations must prioritize the security and privacy of PHI to maintain a high standard of care and ensure the well-being of their patients.
Confidentiality and Security Measures for Protected Health Information (PHI
Implementing robust security measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits is essential for maintaining the confidentiality and security of protected health information (PHI). These measures help to prevent unauthorized access, disclosure, and alteration of PHI, ensuring that sensitive patient data remains protected.
To ensure the utmost security of PHI, organizations should consider the following:
- Encryption: Encrypting PHI helps to protect it from unauthorized access by converting it into unreadable code.
- Access Controls: Implementing access controls, such as strong passwords and user authentication, limits access to PHI to only authorized individuals.
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular audits allows organizations to identify and address any vulnerabilities or breaches in their security systems.
By implementing these security measures, organizations can ensure the confidentiality and security of PHI, protecting patients’ privacy and maintaining their trust.
Now, let’s discuss the distinction between protected health information and consumer health information.
Distinction Between Protected Health Information and Consumer Health Information
We will now explore the distinction between protected health information (PHI) and consumer health information (CHI) and how they differ in terms of privacy and legal regulations. Protected health information refers to any individually identifiable health information that is created, received, stored, or transmitted by a covered entity or business associate. This includes information such as medical records, health insurance claims, and billing information. On the other hand, consumer health information refers to health-related information that individuals generate and share themselves, such as fitness tracker data or information shared on social media platforms. While both types of information have privacy considerations, protected health information is subject to stricter legal regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Now, let’s delve into the topic of electronic protected health information (ePHI) and its significance in healthcare privacy and security.
Electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI
A significant amount of electronic protected health information (ePHI) is stored and transmitted through various electronic systems in healthcare organizations. This poses challenges in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI. To address these challenges, healthcare organizations must implement robust security measures and adhere to relevant regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Key considerations regarding ePHI include:
- Security measures: Encryption, access controls, and audit logs are essential for protecting ePHI from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Data storage: Healthcare organizations must ensure that ePHI is stored securely in encrypted databases or systems.
- Data transmission: Secure protocols, such as secure email or virtual private networks (VPNs), should be used when transmitting ePHI.
Considerations for Developers Regarding Protected Health Information (PHI
Developers must carefully consider the intricacies of handling and safeguarding Protected Health Information (PHI) to ensure compliance with privacy and security regulations. PHI includes any individually identifiable health information that is created, received, maintained, or transmitted by healthcare providers. It is crucial for developers to implement strong security measures to protect PHI from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. This includes encryption of data at rest and in transit, regular vulnerability assessments, and access controls. Developers must also ensure that they adhere to the principles of data minimization and only collect and store the minimum necessary PHI for the intended purpose. Additionally, they should implement audit logs and monitoring systems to detect and respond to any security incidents promptly. By taking these considerations seriously, developers can contribute to a safe and secure environment for PHI, promoting trust and compliance within the healthcare industry.
Covered Entities and Business Associates Under HIPAA
It is important to understand the roles and responsibilities of covered entities and business associates under HIPAA in order to ensure compliance with privacy and security regulations.
- Covered Entities:
- Healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses.
- Responsible for protecting the privacy and security of individuals’ protected health information (PHI).
- Must implement safeguards to prevent unauthorized access or disclosure of PHI.
- Required to provide individuals with notice of their privacy practices and obtain their consent for certain uses and disclosures of PHI.
- Business Associates:
- Individuals or entities that perform functions or services on behalf of covered entities.
- Must enter into a written agreement with covered entities to ensure they comply with HIPAA regulations.
- Required to implement appropriate safeguards to protect PHI.
- Accountable for reporting any breaches of PHI to the covered entity.
Understanding these roles and responsibilities is crucial for both covered entities and business associates to maintain the trust and privacy of individuals’ health information. Compliance with HIPAA regulations ensures the protection of PHI and upholds the standards of privacy and security in the healthcare industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, protected health information (PHI) refers to any individually identifiable health information that is created, received, maintained, or transmitted by a covered entity or business associate. Access to PHI is strictly regulated to ensure confidentiality and security. It is important for developers to consider privacy and security measures when handling electronic PHI (ePHI). Overall, protecting PHI is crucial to maintaining the privacy and trust of individuals seeking healthcare services.